Implementing Agency: College of Agriculture, Kyrdemkulai, Meghalaya
Biodegradation or decomposition is the process of changing biodegradable materials into a useful resource. Decayed organic material (compost) is commonly used as manure or fertilizer for growing plants. It improves soil structure and provides nutrients. Agro-ecological farming methods are gaining popularity because they enhance environmental sustainability. These rely on ecological processes to sustain the health of soil and they treat farming as an integrated, holistic, interconnected process of food production by optimizing the farm in design and closely knit nutrient and resource recycling. Instead of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, compost, green manure, and bone meal are key ingredient in organic farming along with non-chemical modes of pest and disease control. Consciousness of healthy lifestyle has seen organic farm production and trade emerging as an important sector in India as in other parts of the developing world.

Looking at the above prospective, NECTAR has supported this project with the following objectives:
- Demonstration of agri-waste management technology and training in product development & design prototyping for the raw material, finished merchandizing and value-added production line.
- Recycling of biomass, agricultural by-products, forest litters and other residues to manures and compost.
- Training to rural youth, tribal and resource poor farmers in rural bio entrepreneurship through vermi-composting.
- Training to rural youth, tribal and resource poor farmers for value added products of Agriculture.
Outcome and People Benefited: -
- Production of different customized manure has been started at Biomass Recycling Unit.
- A training programme was organised on ‘Integrated farming systems and local resources recycling for integrated natural resources Management and Atma Nirbhar Bharat’ where more than 40 participants from Meghalaya BASIN Development Agency (MBMA) including their officials and farmers from East Garo Hills, East Khasi Hills and Ri-Bhoi district were attended following a hands-on training.
- Another training programme was organized on 7-9 December 2021 for the skill development of rural youth, small and marginal farmers of NEH region where 70 major participants were from East Garo hills, East Khasi hills, West Jaintia hills and Ri Bhoi district including farmers from Nongstoin village have also participated to build up their skill in the area of waste recycling following a hands-on training for the preparation and mixing of different substrates in the pits for the preparation of different types of customized manure.
Implementing Agency:Dimapur, Nagaland
 Honey is a health food loved by people over the generations for its many health benefits. Honey and beekeeping have a long history in India. India is one the major exporter of Honey. As per APEDA, India has exported 59,999.24 MT of natural honey to the world worth Rs. 716.13 Crore to United States, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Bangladesh and Canada during the year of 2020-21. North East Region of India and Maharashtra are the key areas for natural honey production.
Honey is a health food loved by people over the generations for its many health benefits. Honey and beekeeping have a long history in India. India is one the major exporter of Honey. As per APEDA, India has exported 59,999.24 MT of natural honey to the world worth Rs. 716.13 Crore to United States, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Bangladesh and Canada during the year of 2020-21. North East Region of India and Maharashtra are the key areas for natural honey production. 
North-eastern Region (NER) of India has natural advantage of no usage of harmful pesticides by farmers and hence the product produced will have added value as organic. Nagaland, due to the availability of lush forest coverage, is a cradle for a huge variety of flowering plants coupled with ideal climatic conditions and hence is a home to a variety of honeybee species. From rock bees that abounds in the seemingly unhospitable and rugged mountains to Apis cerena bees that set up their communal residence in the midst of friendly Naga homes, to the trigona/ Melipona species (stingless bees) are found in the wild and also reared in the homestead hives. Honey production in the state was 440 MT during 2020-21. Nagaland is the leading honey producing State in the whole of North East Region.
Beekeeping or bee farming is a widely practiced in the State and is a growing trend which has become way of life for many in the State. Beekeeping is done mostly for honey production in the State and ensures supplementary income for the beekeepers. In addition, bees do not compete with the crops for the resources and does not require high capital investments, infrastructure or land for their farming. While Bees are reared mostly for their honey production, their role in increasing productivity cannot be denied as all bees are pollinators which are essential for majority of the crops. It is said that insect driven pollination and nectar gathering from large areas, contributes to a more diverse, sustainable ecosystem and thus, Bee keeping have an important role to play in our endeavor to ensuring a sustainable environment. State not only has an ideal climate required for bee-rearing, but the tribal communities also have very rich traditional knowledge centring, among other things, around honey. Various Naga tribes have been rearing honey since a long time, and honey has been a must as an ingredient in various traditional Naga recipes. Traditionally, bees have been reared since time immemorial in crude wooden or log hives, while modern beekeeping involves rearing them in scientifically designed hives with scientific management practices.
However, by the traditional method of beekeeping many wild colonies of bees are destroyed. This can be prevented by scientific bee keeping method by raising bees in boxes, so that colonies are not destroyed as there is separate section of fruit/egg and honey. Hence only honeycomb is extracted, and colonies are not affected.
 To promote scientific beekeeping and support apiary expansion in the State, NECTAR has initiated various project with State Missions and various NGOs. To avoid problems such as the loss of beehives due to theft, vandalism, fires, weathering etc. and to save space and cost in construction of wooden beeboxes, NECTAR has supported NBHM for construction of 1000 underground Concrete Hives in Mima village, Kohima district and 500 underground Concrete Hives in Runguzu village, Phek district leading to production of 6T of honey valued at Rs.21 lakhs. Center has also supported ECS, an NGO for distribution of 1700 innovative bee boxes among the beekeepers of Tuensang district leading to production of 7T of Honey. 675 bee boxes and accessories like extractor, strainer, gloves etc were also supported to Kiding Self Help Group located in Kiding village, Phek District, and lead to production of 1.5T of honey.
To promote scientific beekeeping and support apiary expansion in the State, NECTAR has initiated various project with State Missions and various NGOs. To avoid problems such as the loss of beehives due to theft, vandalism, fires, weathering etc. and to save space and cost in construction of wooden beeboxes, NECTAR has supported NBHM for construction of 1000 underground Concrete Hives in Mima village, Kohima district and 500 underground Concrete Hives in Runguzu village, Phek district leading to production of 6T of honey valued at Rs.21 lakhs. Center has also supported ECS, an NGO for distribution of 1700 innovative bee boxes among the beekeepers of Tuensang district leading to production of 7T of Honey. 675 bee boxes and accessories like extractor, strainer, gloves etc were also supported to Kiding Self Help Group located in Kiding village, Phek District, and lead to production of 1.5T of honey.
 NECTAR has also supported project on transfer of knowledge on scientific bee management and apiary expansion in Mokokchung District with NBHM under which more than 520 bee boxes have distributed and 2 batches of training covering aspect of apiary management techniques, post-harvest management, value addition, marketing skills. The activity has led to production of 35T of honey in State. To further strengthen the sector, NECTAR is supporting establishing honey testing laboratory at Dimapur, Nagaland. By setting up lab in Dimapur, honey samples from North eastern states can be tested and different types of honey can be analysed in NE itself. The test report of honey samples will be documented and that way a database would be created which will help bee researchers and bee scientists for research. Proper analysis will ascertain product quality produced by different bee species in NER and this help in checking compliance with national and international food standard specifications and nutrient labelling. The project will be merged with activity of intervention on rock bee hunting in Nagaland under which 75 rock bee hunters will be trained professionally in scientific lines and skill in honey & Wax trade to support innovative techniques of Rock bee hunting in enhancing productivity and quality in an environmentally sustainable manner.
NECTAR has also supported project on transfer of knowledge on scientific bee management and apiary expansion in Mokokchung District with NBHM under which more than 520 bee boxes have distributed and 2 batches of training covering aspect of apiary management techniques, post-harvest management, value addition, marketing skills. The activity has led to production of 35T of honey in State. To further strengthen the sector, NECTAR is supporting establishing honey testing laboratory at Dimapur, Nagaland. By setting up lab in Dimapur, honey samples from North eastern states can be tested and different types of honey can be analysed in NE itself. The test report of honey samples will be documented and that way a database would be created which will help bee researchers and bee scientists for research. Proper analysis will ascertain product quality produced by different bee species in NER and this help in checking compliance with national and international food standard specifications and nutrient labelling. The project will be merged with activity of intervention on rock bee hunting in Nagaland under which 75 rock bee hunters will be trained professionally in scientific lines and skill in honey & Wax trade to support innovative techniques of Rock bee hunting in enhancing productivity and quality in an environmentally sustainable manner.
Outcome and People Benefited: -
NECTAR has made significant impression in expanding the honey production in the State by supporting more than 4,390 no. of bee boxes to number of beekeepers leading to production of more than 45T honey, imparting training, marketing through e portals, setting up of lab and intends to expand the support in other States for overall development and spreading sweetness in NER.



Implementing Agency: - Urban Harvest, Guwahati

The growing population and the increasing pressure on soil for more yield has resulted in the degradation of soil. The soil in certain areas has been degraded to an extent that it would take years for the soil to rejuvenate. But the inability of the soil to produce more yields shouldn’t be the reason for starvation in this state and this nation. Hence, here comes a new innovative system to reduce the pressure on soil and at the same time produce enough yields. To be more precise, this new system will have a higher magnitude of yield as compared to the traditional technique of cultivation on soil.

The Hydroponic system of Crop Cultivation, where crops are cultivated in water and not on soil, provides the advantage of growing crops anywhere irrespective of soil quality. Also, this system might alert a few regarding possible water shortage problems during this process of cultivation. But the reality of this system beats the odds on even water shortage. It implies that the water is reused instead of completely draining the water out after one use. Reusing of water has been made possible with the addition of nutrients in the water that run past the roots of the crops thus helping the crops take up nutrients from the water. Adding to that, this system of cultivation aims at producing crops of high value in terms of nutrition, market value etc. The productivity of the crops grown is active throughout the year and hence it promises to make a considerable profit in terms of business and also in providing nutritious products to the population. And with the increasing demand of organic food in the society, the sales of the yield have the capacity to skyrocket.
The environment plays a pivotal role in the growth of crops. It has an influence on crop health, thus on the harvest. And since, in the hydroponic system, the crops will be cultivated in a greenhouse, the environment can be well regulated according to the pace of the growth of the crops. Therefore, there will be less infestation of pests and diseases which will ensure a mere use of harmful pesticides. This will assure the crop to be more healthier and full of nutrition. As a result, we receive good quality crops and almost no loss of crops.

The hydroponic system produces a maximum of 60% to minimum of 10% more per acre. When narrowed, we find that the amount of tomato produced (tons per acre) is only 10-12 on soil but increases to 100-180 when cultivated in the hydroponic system.
This data not only defines an increase in the yield but also draws a fine border on the land requirement. To be brief, this data indicates that even in small patches of land, the yield can be maximized. Hence, it provides an opportunity for various small scale to big scale businesses to maximize their sources of profit. Therefore, this data outlines the chances of high yield as well as economic profit.
The project was implemented on a pilot basis by the promoter to ascertain of its viability for taking up on a large scale in the region which has found success. With the above data we can estimate that in a land of approx. 1500 sq.ft. we can get a profit of maximum 40%. This rate is immensely higher than the traditional system of cultivation. This is a very much newer concept in this part of our country. With this project we can revolutionize the cultivation practices and can carry out intensive and high turnover production with healthy and organic harvest
Outcome and People Benefited: -
NECTAR, has taken the initiative to make it a success by providing all sorts of help which in turn not only provide healthy, nutritional and organic consumables to the people but also socio - economic growth of this region.
Implementing Agency: - Water Bank Foundation, West Mumbai
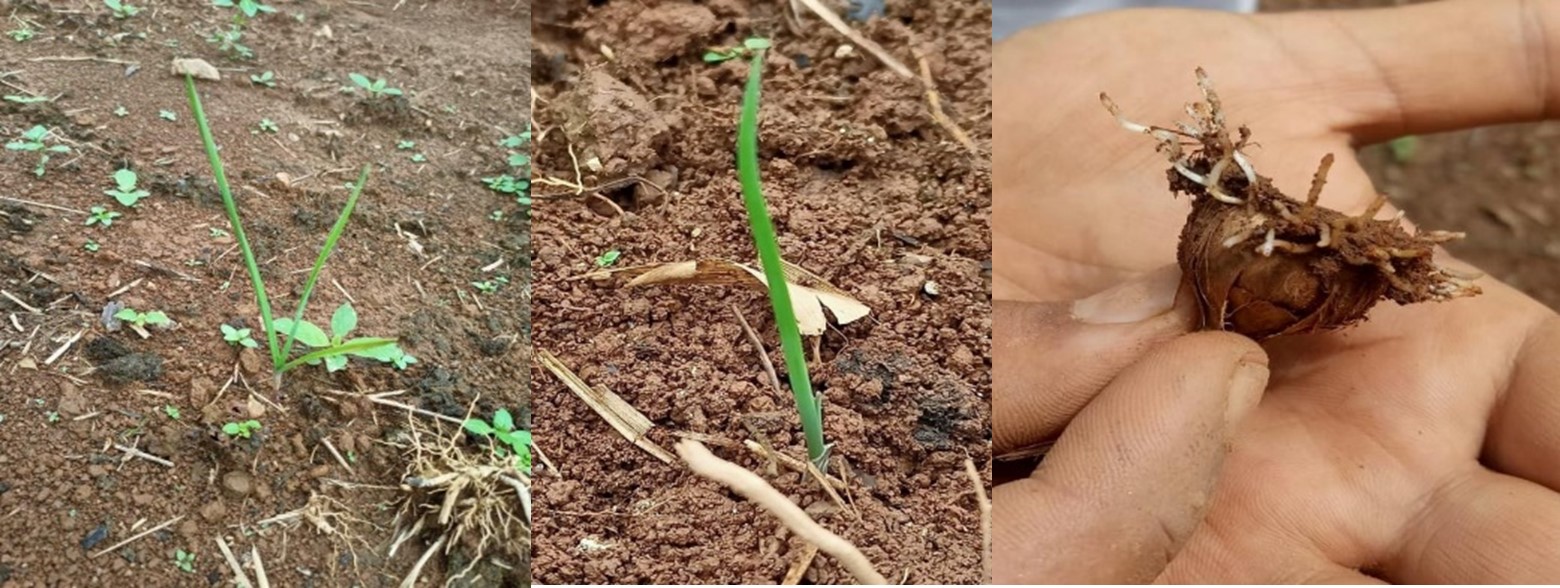
Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) a perennial herb belongs to Iris family Iridaceae and is the most expensive spice in the world known for its aroma and colour and used for flavouring and colouring and in medicinal, pharmaceutical industries. The colour, flavour and aroma of saffron are mainly due to crocin, picrocrocin and safranal, respectively. Due to very high crocin content and rich aroma, the Kashmir saffron is famous worldwide and commands a premium price over the saffron available from Spain or Iran.
Total world production of saffron is around 300 tons per year. Iran, India, Spain and Greece are the major saffron producing countries with Iran occupying the maximum area and contributing about 88% of world’s saffron production. Though, India occupies the 2nd largest area but produces approximately 7 per cent of the total world production. Jammu-Kashmir is the only state in India where saffron is produced. The total area under saffron cultivation in J&K is 3715 ha with production and productivity of 16 MT and 3.0 – 4.0 kg/ha, respectively. Saffron in J&K is primarily cultivated in four districts (Pulwama, Budgam, Srinagar, Kishtwar) with 86% saffron farming system in heritage site of Pampore over 3200 hectares. Pampore being peri-urban is under threat of commercialization /colonization therefore extending saffron cultivation in new potential and nontraditional areas of J&K will provide more sustainability to the saffron cropping system. This will help to further improve overall saffron production of J&K keeping in view National demand of 100 M.T besides providing livelihood security to the marginally poor farmers of J&K. (Ref. https://iiim.res.in/saffron-production/)
Owing to the importance of the crop for its national market demand and export potential the crop was successfully introduced and grown at Sikkim by Water Bank Foundation in August 2020 in a trial basis under a grant-in-aid support on Technology Outreach and Services Scheme (TOSS) from NECTAR.
The pilot project has yielded successful results in Yangyang village of South Sikkim, which produced its first crop of saffron in September 2020. It was grown across 1,000 square metres. Under a motto Mission Atmanirbhar India the trust has further extended the trial in Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya due to its suitable climatic condition, under another grant-in-aid support from NECTAR, which will finally aimed to be on commercial scale in different areas of the North-Eastern Region of India. Currently pilot projects are taken up in Meghalaya and Arunachal Pradesh
Introduced Saffron to the NER of India’s geographical areas in its unique climate will give farmers to take up Saffron cultivation to meet the domestic demand as well as export the spices as well. According to the Trade Promotion Council of India, prior to 2020, India was the fourth-largest importer of Iranian saffron and had imported saffron worth USD 18.30 million from Iran. The introduction of Saffron farming in NER will enhance in reduce of import from Iran and contribution of the local farmers income generation.

In continuation to the support for livelihood, skill development and assisting market linkages for North Eastern products, NECTAR has supported beekeeping activity in Kiding village, Tuensang Nagaland, towards expansion of Honey growers of Tuensang. 135 honey growers were facilitated by providing with 675 improved bee harvesting boxes and accessories etc. The project is giving regular source of income opportunity to many farmers of the region.

पृष्ठ आखरी अपडेट : 26-03-2025 - 21:17